Introduction: The Algorithmic Imperative of External Links
In the ecosystem of Search Engine Optimization (SEO techniques), external links—specifically, backlinks—are not merely connections between web pages; they represent the fundamental structural units of authority and trust. For search algorithms, an external hyperlink from a high-quality source functions as a crucial "vote of confidence," signaling to the search engine that the linked-to content is valuable, relevant, and authoritative.
This technical article is designed for beginners and intermediate practitioners seeking a deep understanding of how these signals are quantified, how to employ advanced acquisition strategies, and how to maintain the integrity of a link portfolio through proactive reputation management. We will dissect the foundational algorithms that govern link equity transfer, explore data-driven strategies for link acquisition, and outline the technical specifications necessary to build a robust, sustainable domain authority that withstands algorithmic updates.
The path to achieving dominant search visibility requires precision, strategic execution, and adherence to technical best practices. The goal is not just to acquire links, but to engineer a high-authority backlink profile that aligns perfectly with Google's quality guidelines, ultimately maximizing the transfer of PageRank.

The Core Technical Foundation: PageRank and Link Equity Transfer
To master external link building, one must first understand the core algorithm that quantifies link authority.
The PageRank Algorithm: A Mathematical Model of Authority
Official Product/Technology Name: PageRank (PR)
Developer Company Information: Developed by Google co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1996 while they were Ph.D. students at Stanford University. PageRank was the foundational technology upon which the Google search engine was built.
PageRank is a link analysis algorithm that assigns a numerical weighting to every element (page) in a hyperlinked set of documents (the World Wide Web) to measure its relative importance within that set. It operates on the principle of the "random surfer model," which posits a hypothetical user clicking on links randomly.
Precise Technical Specifications and the Damping Factor
The algorithm calculates a probability distribution, typically between 0 and 1, representing the likelihood that the random surfer will arrive at any particular page. This value, or rank, is calculated iteratively across the entire index.
The simplified mathematical formula for PageRank of a page A is:
PR(A) = (1-d)/N + d × (Σ PR(Ti)/L(Ti))
Where:
- PR(A): The PageRank value of page A.
- d: The damping factor (typically set to 0.85).
- N: The total number of pages in the network.
- BA: The set of pages (T1, T2, ...) that link to page A.
- PR(Ti): The current PageRank of the linking page Ti.
- L(Ti): The number of outbound links on page Ti.
The damping factor (d=0.85) is a critical component. It models the 15% probability (1-d) that the hypothetical random surfer will stop clicking the current page's links and "teleport" to a random page in the index. This mechanism prevents PageRank from being trapped in dead-end pages (known as "dangling nodes") or infinite loops, ensuring the calculation converges to stable, meaningful values typically within 50 to 100 iterations.
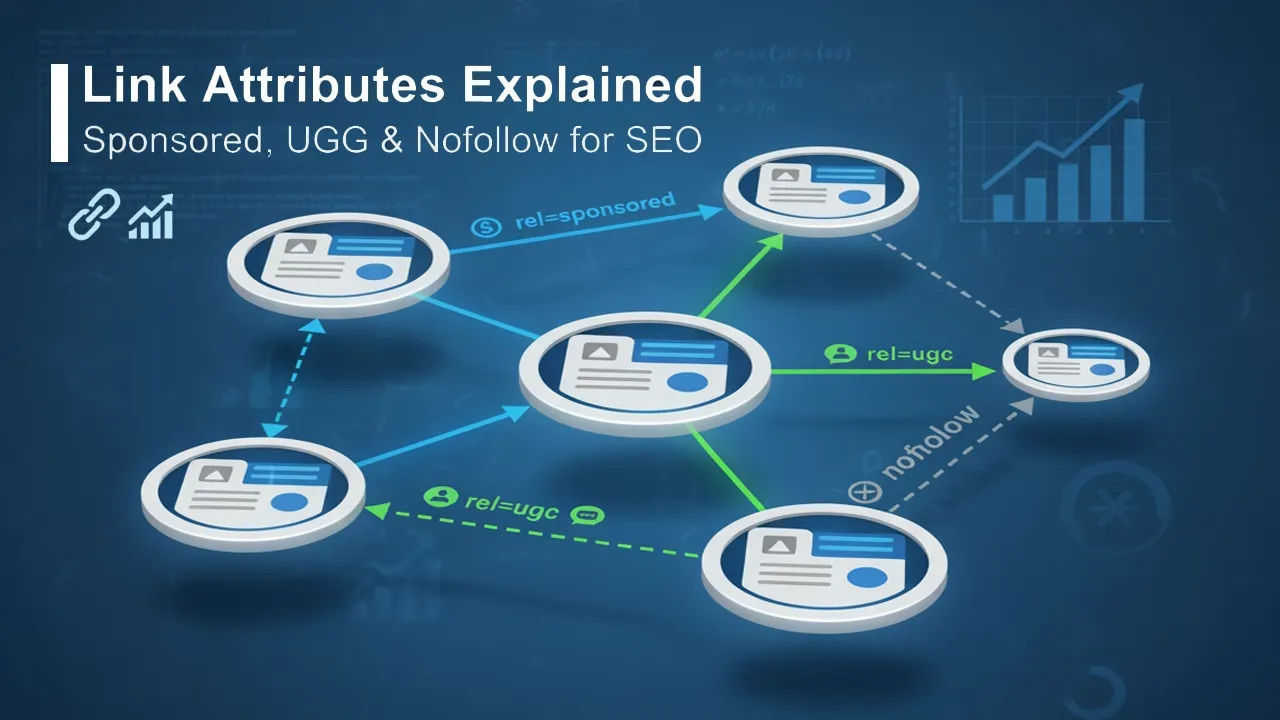
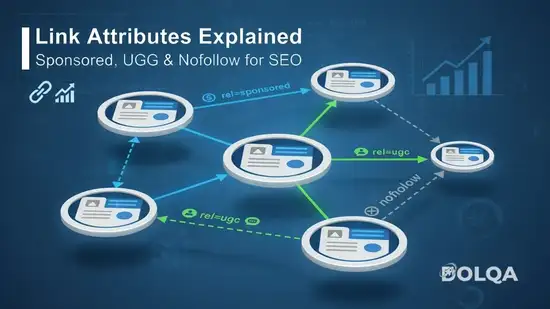
Link Attributes: Directives vs. Hints
The way search engines process link equity transfer is also dictated by HTML link attributes, which have undergone significant updates.
| Attribute | Technical Specification (HTML Syntax) | Purpose | Update (March 2020) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nofollow | rel="nofollow" | Signals that the linking page does not endorse the target page. Used traditionally for paid or unvetted links. | Treated as a Hint: Google may choose to crawl the link and/or use it for ranking purposes. |
| Sponsored | rel="sponsored" | Preferred for links that are advertisements, paid placements, affiliate links, or compensation agreements. | Treated as a Hint: Allows Google to better categorize link intent. |
| UGC | rel="ugc" | Recommended for links within User-Generated Content (e.g., blog comments, forum posts, discussion boards). | Treated as a Hint: Helps distinguish user contributions from editorial content. |
System Compatibility and Versions: These attributes are supported by standard HTML5 using the <a> element (e.g., <a href="URL" rel="sponsored ugc">Link Text</a>). The 2019 announcement and 2020 roll-out of treating these as "hints" marks a significant evolution in Google's algorithms, allowing the system to leverage these links for discovery and context even if authority transfer is restricted or discounted. Proper use of rel="sponsored" is still necessary to maintain compliance with Google's guidelines against link schemes.
Advanced Backlink Acquisition Strategies (SEO techniques) and Performance Data
Effective external link acquisition is not accidental; it is a systematic deployment of high-value SEO techniques rooted in data and targeted outreach. The focus must always be on quality and relevance, as consistently emphasized by Google and proven by industry research.
Content-Centric Link Earning and Linkable Assets
The cornerstone of modern link building is the creation of "linkable assets"—content so valuable, unique, or comprehensive that it naturally attracts backlinks.
Original Research and Data-Driven Content: Content featuring proprietary research, industry statistics, or comprehensive surveys inherently earns links because it becomes a primary citation source. High-quality data ensures the linking site meets the E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) criteria for their readers.
Evergreen Content: Content that remains relevant and valuable over time (e.g., definitive guides, tutorials, resource pages) continues to attract links long after publication. The source documentation highlights the power of refreshing and updating evergreen content to maintain its link equity attraction potential.
Performance Statistics: Studies show a strong positive correlation between focused link-building efforts and business results. In fact, over 78.1% of SEO professionals report a positive Return on Investment (ROI) from their structured link-building campaigns, validating it as a high-yield SEO technique.
Strategic Outreach and Digital PR
Outreach involves building relationships with high-authority webmasters in your niche, offering them value in exchange for a link.
Digital PR: The Most Effective Tactic
Recent industry data suggests that Digital PR is the most effective link-building tactic, chosen by 48.6% of SEO experts. Digital PR focuses on creating newsworthy content (e.g., press releases for real milestones, data visualizations, expert commentary) to earn mention and links from high-tier media and news outlets. These links, often from domains with extremely high Domain Authority/Rating (DR), provide a significant authority boost.
Broken Link Building
This SEO technique is highly technical and efficient. It involves:
- Identifying a reputable website (high DR).
- Using a tool (like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog) to crawl their site and identify pages containing 404 errors (broken links).
- Determining the topic of the broken page.
- Creating a superior piece of content on that exact topic on your domain.
- Contacting the webmaster, notifying them of the broken link, and professionally suggesting your resource as a relevant, updated replacement.
This strategy offers value (fixing a technical issue for the site owner) while securing a high-quality link.
Cost and Time Investment
Link building can be costly, reflecting the high perceived value of these backlinks. The average acceptable price for acquiring one high-quality link (e.g., through a paid guest post arrangement) is around $609, emphasizing the need to maximize the quality of every single acquisition. Furthermore, SEO professionals indicate that the impact of a link-building campaign typically requires a processing time: 46.6% see results within 1 to 3 months, with an additional 35.2% seeing results within 3 to 6 months.
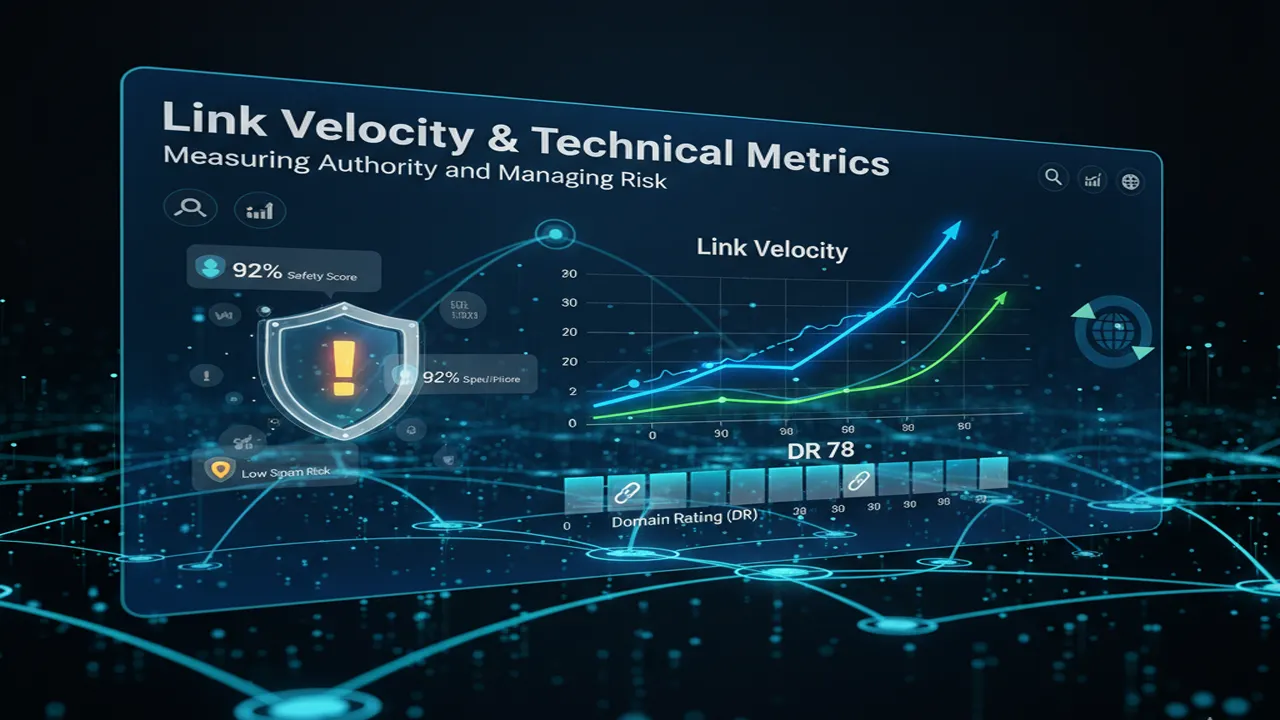 Link Velocity and Technical Metrics" data-rotate="0" data-proportion="true" data-align="center" data-percentage="95%,auto" data-size="95%,auto" data-file-name="image_68e68161f050f_1759936865.png" data-file-size="1076074" data-origin="95%,auto" origin-size="1280,720" style="width: 100%; height: auto;">
Link Velocity and Technical Metrics" data-rotate="0" data-proportion="true" data-align="center" data-percentage="95%,auto" data-size="95%,auto" data-file-name="image_68e68161f050f_1759936865.png" data-file-size="1076074" data-origin="95%,auto" origin-size="1280,720" style="width: 100%; height: auto;"> Technical Metrics and Link Velocity for Scaling
Effective link management requires the use of third-party metrics to quantify authority and monitor growth rate, ensuring the strategy remains natural and safe from algorithmic scrutiny.
Quantifying Authority: Domain Rating (DR) and URL Rating (UR)
Since Google ceased publicly updating its official PageRank metric, third-party SEO tool developers created proprietary metrics to estimate a domain's overall authority and link equity potential.
| Metric | Developer/Tool | Definition | Performance/Use Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain Rating (DR) | Ahrefs | Measures the strength of a website's overall backlink profile on a logarithmic scale from 0 to 100. | 64.1% of SEO experts use Ahrefs' DR and UR as their primary authority metrics. |
| Domain Authority (DA) | Moz | Predicts how likely a website is to rank in search results, also on a logarithmic 0-100 scale, based on proprietary factors. | Used widely for competitive analysis and target selection. |
| Citation Flow (CF) / Trust Flow (TF) | Majestic | CF measures the volume of links; TF measures the quality (trustworthiness) of those links. | Used for deeper link profile analysis and spam detection. |
These third-party tools (Ahrefs, Moz, Semrush) are considered essential for strategic execution. For instance, Ahrefs leads the market, used by 59.1% of respondents in a recent industry survey. When seeking backlinks, it is standard technical practice to target domains with a Domain Rating (DR) of 30+ or higher, as recommended for competitive niches, to ensure maximum link equity transfer.
Optimizing Link Velocity and Growth Rate
Link velocity is the rate at which a website acquires new links or referring domains over a set period. It is a critical factor that search engines monitor to distinguish between organic growth and manipulative link schemes.
Natural vs. Manipulative Growth: A sudden, massive spike in link acquisition from unrelated or low-quality sources is a classic characteristic of an unnatural link pattern. This signals potential manipulation and increases the risk of a manual or algorithmic penalty.
Gradual and Consistent: A healthy link velocity involves a gradual, steady increase in link acquisition over time, commensurate with the website's age, content publication frequency, and brand visibility. For a new site, jumping from 1-2 referring domains per month to 15-20 in a single month would appear highly suspicious. Established, high-traffic websites are naturally expected to sustain a much faster velocity rate.
Content Correlation: Link velocity should ideally correlate with content promotion and news cycles. A surge following a major Digital PR campaign is expected and natural; an unexplained surge is not.
Proactive Digital Reputation Management
Effective SEO techniques must include robust reputation management focusing on the quality and integrity of the external link profile. A single, toxic link can potentially degrade the authority built by dozens of high-quality backlinks.
Backlink Auditing and Risk Mitigation
A comprehensive backlink audit is a periodic technical review of all incoming links to identify toxic or low-quality sources. A link is considered toxic if it originates from:
- Spam Networks: Private Blog Networks (PBNs), link farms, or known scraper sites.
- Unrelated/Irrelevant Domains: Sites with no topical relevance to your business.
- Malware or Pornographic Domains: Links that pose explicit safety or quality risks.
- Over-optimized Anchor Text: Links using aggressive, exact-match keywords that violate Google's quality guidelines.
The Disavow File Protocol
The technical specification for mitigating risk is the Disavow Tool, a utility provided by Google Search Console.
Technical Process: When toxic links are identified, they are compiled into a plain text file (
.txt) where each line specifies either a single URL to disavow or, more commonly, an entire domain (e.g.,domain:spamsite.com). This file is then uploaded to Google Search Console.Purpose: By uploading this file, the webmaster instructs Google to ignore the specified links when calculating PageRank and assessing the site's authority. This serves as documented evidence to Google that the site owner does not endorse or wish to benefit from the toxic links.
Usage Context: Usage of the Disavow Tool is declining among experts; only 39.0% report using it. This is partly due to Google's improved ability to automatically identify and discount low-quality links. However, it remains the essential defense mechanism against large-scale negative SEO attacks or for correcting legacy, manually built spam.
Reputation Building Beyond Links
True reputation management extends beyond managing the technical backlink profile. The technical search algorithms increasingly value unlinked brand mentions—instances where a company is mentioned on a high-authority site without a direct hyperlink. Approximately 80.9% of SEO specialists believe these unlinked brand mentions influence organic search rankings, suggesting that the algorithm correlates brand recognition with authority and trustworthiness (a key component of E-E-A-T). Digital PR and high-visibility media features are the primary vehicles for generating these valuable, non-link signals.
Conclusion: Engineering Sustainable Authority
The pursuit of high search rankings through external link building is a complex technical discipline that requires a mastery of both mathematical models and strategic outreach. By understanding the core mechanics of PageRank, applying data-driven SEO techniques like Digital PR and strategic broken link building (as outlined by industry best practices and reinforced by sources like Ranked), and maintaining vigilant reputation management through continuous backlink auditing, practitioners can construct a robust, defensible foundation of domain authority.
The technical specifications—from the 0.85 damping factor to the correct implementation of rel="sponsored" hints—are not arbitrary rules but the language of modern search algorithms. Your success hinges on the technical quality and consistency of your backlinks and link acquisition velocity.
We encourage you to perform a complete technical audit of your existing backlink profile immediately. Which links are passing maximum equity, and which ones present an unnecessary risk? Leveraging proprietary tools like Ahrefs is not optional; it is essential to measure your authority (DR) and benchmark your link velocity against competitors. Start engineering your authority today.



Comments (0)
Leave a Comment
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!